10.2.2 Filters
You can place filters in the midst of an integration pipeline to allow or disallow messages from proceeding to the next step in the flow, as shown in figure 10.3.
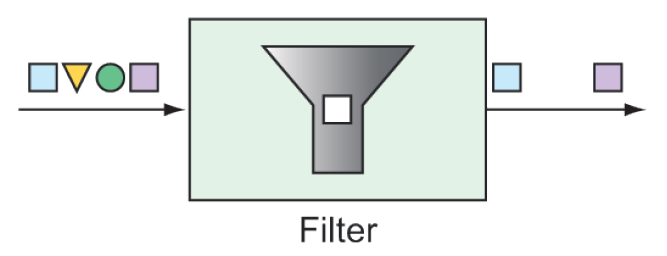
Figure 10.3 Filters based on some criteria allow or disallow messages from proceeding in the pipeline.
For example, suppose that messages containing integer values are published through a channel named numberChannel, but you want only even numbers to pass on to the channel named evenNumberChannel. In that case, you could declare a filter with the @Filter annotation like this:
@Filter(inputChannel="numberChannel",
outputChannel="evenNumberChannel")
public boolean evenNumberFilter(Integer number) {
return number % 2 == 0;
}Alternatively, if you’re using the Java DSL configuration style to define your integration flow, you could make a call to filter() like this:
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow evenNumberFlow(AtomicInteger integerSource) {
return IntegrationFlows
...
.<Integer>filter((p) -> p % 2 == 0)
...
.get();
}In this case, you use a lambda to implement the filter. But, in truth, the filter() method accepts a GenericSelector as an argument. This means that you can implement the GenericSelector interface instead, should your filtering needs be too involved for a simple lambda.
